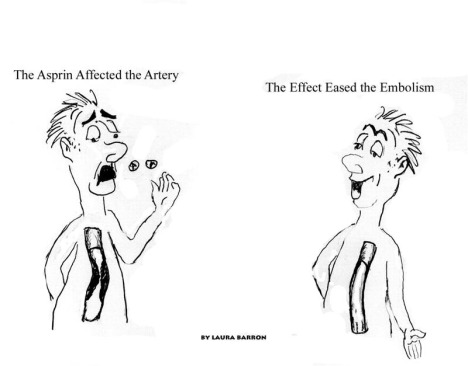
This is a confusing issue, and can easily be decided – effect is a noun, and affect is a verb.
But sometimes there are special cases where it isn’t so black and white. These are the some points to help.(See what each word means below)
Affect – as a verb: to act upon; as an adjective: influence by an outside force
Also it gets a little daunting when it is used in the medical practice. Affect can be used when we are talking about attacking or infecting such as a disease. Exp: Fever can affect the heart. or …The disease did not affect her skin.
It is influencing. Use the word ‘influence’ in place of affect to see if it works. Or try ‘change’ – then it is more likely effect.
Effect – as a noun: result, consequence; as a verb: to bring about
Think of it meaning result. If you have a word ‘the’ or ‘an’ in front, (also take, into, any, and, no) it is most likely effect. Exp: The effect of hot water on ice is…. or…..It is an effect of the following….
Effect can sometimes/but rarely used as a verb. Such as creating. If you can replace “result”, or “to bring about” for “effect” – But when in doubt, use Affect.
If you were to try to place ‘result’ in for the sentence used in Affect – The disease did not result her skin. It doesn’t make sense.
To make things more complicated, Effect can be used in scientific areas such as when you are talking about ’cause and effect’ – Who was the doctor who effected a cure for polio?
Lastly, if you understand all the above, then you should get this defining line: IF YOU AFFECT A SITUATION, YOU HAVE AN EFFECT ON IT.
Affect (fromyourdictionary.com)
- To have an influence on or effect a change in: Inflation affects the buying power of the dollar.
- To act on the emotions of; touch or move.
- To attack or infect, as a disease: Rheumatic fever can affect the heart
Effect (fromyourdictionary.com)
- Something brought about by a cause or agent; a result.
- The power to produce an outcome or achieve a result; influence: The drug had an immediate effect on the pain. The government’s action had no effect on the trade imbalance.
- A scientific law, hypothesis, or phenomenon: the photovoltaic effect.
|
- Advantage; avail: used her words to great effect in influencing the jury.
- The condition of being in full force or execution: a new regulation that goes into effect tomorrow.
-
- Something that produces a specific impression or supports a general design or intention: The lighting effects emphasized the harsh atmosphere of the drama.
- A particular impression: large windows that gave an effect of spaciousness.
- Production of a desired impression: spent lavishly on dinner just for effect.
- The basic or general meaning; import: He said he was greatly worried, or words to that effect.
Filed under: Medical Vocabulary | Tagged: affect, anatomy, AVC, effect, judy sullivan, laura barron, medical, words | Comments Off on What’s the difference between Affect/Effect?











 In order to pitch the ball, we will use the
In order to pitch the ball, we will use the